Eczema On Head Under Hair: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Michele Marchand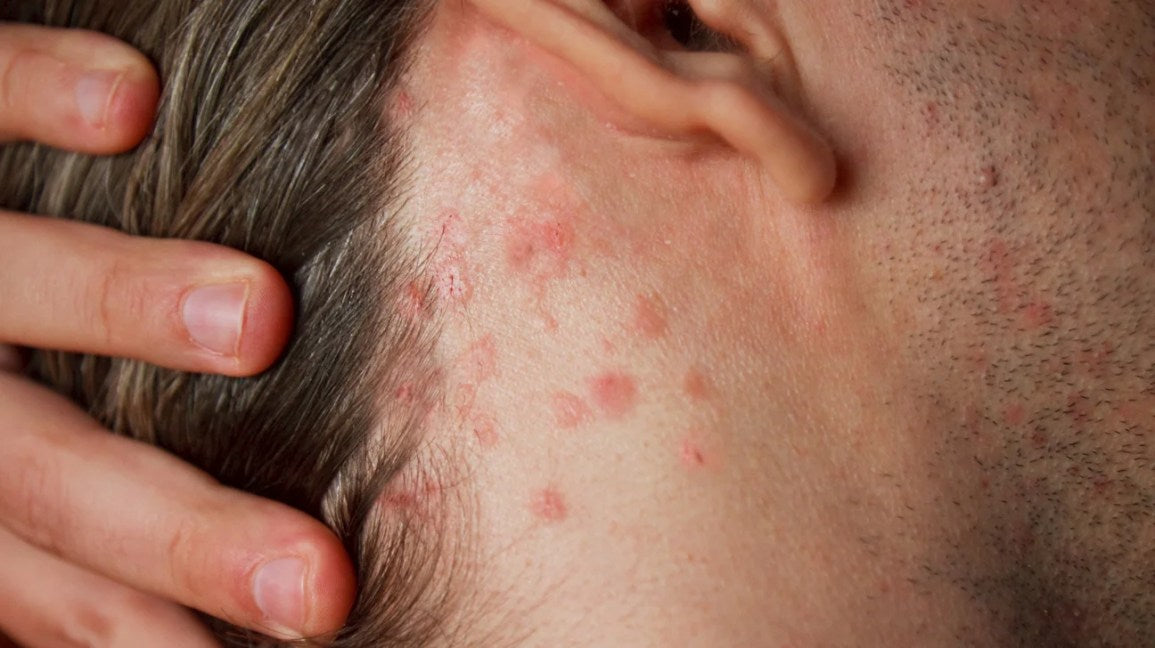
Scalp eczema encompasses a range of inflammatory skin conditions affecting the scalp beneath the hair. These conditions, including atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis, are characterized by symptoms such as redness, itching, flaking, and sometimes oozing or crusting. Scalp eczema can be triggered by various factors such as genetic predisposition, allergens, irritants in hair care products, stress, and fungal or bacterial infections. Understanding the nuances and differences between these types of scalp eczema is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management to alleviate symptoms and improve scalp health.
This article delves into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available for scalp eczema, shedding light on its impact and offering insights for those seeking relief and a better understanding of this common yet challenging condition.
Symptoms and Types of Eczema on Scalp
Eczema itself is a broad term encompassing several types, including atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis, among others.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition characterized by dry, itchy skin and often presents in childhood, with a genetic component contributing to its development. It can affect the scalp, leading to redness, flakiness, and sometimes hair loss due to scratching and irritation.
Seborrheic dermatitis scalp eczema, another common form, typically affects areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest. On the scalp, it can manifest as greasy, yellowish scales or crusts, along with redness and itching. Unlike atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp is associated with an overgrowth of yeast and excessive oil production, which contribute to its characteristic appearance.
 Seborrheic dermatitis. Image credits
Seborrheic dermatitis. Image credits
Contact dermatitis results from skin contact with irritants or allergens, triggering a localized reaction that can include redness, swelling, and blistering. When it affects the scalp, contact dermatitis can cause itching, burning, and a rash, often in areas where hair care products or other substances have been applied.
These various types of eczema differ in their causes, symptoms, and triggers, but they all share the potential to affect the scalp and hair. While atopic dermatitis is linked to genetic and immune factors, seborrheic dermatitis is associated with overgrowth of yeast on the skin and excessive oil production. Contact dermatitis, meanwhile, is provoked by direct contact with substances like soaps, cosmetics, or metals. Despite their differences, these forms of eczema can overlap in symptoms and require tailored approaches to management and treatment. Understanding the distinctions between them is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of scalp eczema and related conditions. Learn more about eczema here.
What Are the Causes of Scalp Eczema?
The causes of scalp eczema vary depending on the specific type. Atopic dermatitis, often linked to genetics, involves skin barrier and immune system dysfunction, heightening sensitivity to environmental triggers like allergens, irritants, or stress, which can provoke scalp eczema flare-ups. Unfortunately, conventional shampoos and hair care products often contain common allergens and irritants that can trigger these flare-ups.
Seborrheic dermatitis scalp eczema is associated with multiple factors, notably an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, naturally present on the skin. Thriving in oil gland-rich areas like the scalp, this yeast prompts an inflammatory response, causing characteristic seborrheic dermatitis symptoms. Simultaneously, excessive sebum production, the skin's natural oil, can worsen this condition by fostering yeast growth and inflammation. Malassezia yeast and sebum contribute synergistically to scalp eczema's persistence and severity, as the yeast's presence irritates the skin, perpetuating inflammation and flaking. You can learn more about Malassezia here.
In contrast, contact dermatitis on the scalp arises from direct contact with substances provoking an allergic reaction or irritation in sensitive individuals. Common triggers include hair care products, dyes, shampoos, and certain metals in hair accessories. The scalp's vulnerability to these irritants leads to itching, redness, and rash development.

Recognizing these diverse causes and triggers is crucial for effectively managing scalp eczema and implementing targeted treatments to relieve symptoms and enhance overall skin health.
Comprehensive Diagnosis: Beyond the Itch
A thorough medical examination is crucial for accurately diagnosing scalp conditions like eczema and distinguishing them from other common issues such as dandruff, dry scalp, psoriasis, and folliculitis. Eczema, including atopic, seborrheic, and contact dermatitis, typically presents with inflammation, itching, and redness on the scalp, often accompanied by flaking or scaling. A key characteristic of eczema is its chronic nature, with flare-ups triggered by various factors like allergens, stress, or certain products.
Dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis are two common scalp conditions often confused due to their similar symptoms, such as flaking and itching. However, they have distinct differences in their underlying causes and behavior, particularly concerning the role of Malassezia yeast. Dandruff primarily involves flaking of the scalp due to an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, which feeds on skin oils (sebum). This overgrowth can lead to irritation and inflammation, contributing to the characteristic flakes associated with dandruff. In contrast, seborrheic dermatitis is a more severe form of scalp inflammation also linked to Malassezia yeast but accompanied by redness, scaling, and sometimes greasy or yellowish crusts. Seborrheic dermatitis typically affects areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest, and is characterized by a more pronounced inflammatory response compared to dandruff.
Dry scalp, another common condition, results from inadequate moisture or oil production on the scalp, leading to itchiness and flaking. Unlike eczema, dry scalp does not typically involve inflammation or intense itching and can be managed with moisturizing treatments.
Psoriasis, characterized by thick, silvery scales and red patches, can also affect the scalp. Psoriasis plaques may extend beyond the hairline onto the forehead or neck and are often accompanied by itching. Unlike eczema, psoriasis lesions are more defined and can be associated with nail changes and joint pain in some cases.
 Scalp psoriasis. Image credits
Scalp psoriasis. Image credits
Folliculitis, an inflammation of the hair follicles, can cause small red bumps or pustules on the scalp. It can result from bacterial or fungal infections, as well as irritation from hair care products or friction. Folliculitis differs from eczema in that it primarily affects the hair follicles rather than the surrounding skin, and it may require specific treatments such as antimicrobial agents or topical steroids.
Given these distinctions, a thorough medical evaluation, including a physical examination and possibly skin biopsies or tests, is essential for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. Effective management relies on understanding the underlying causes and distinguishing features of each scalp condition to provide targeted relief and improve overall scalp health.
How to Treat Eczema on Scalp
Treating the three different types of scalp eczema - atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis - involves a multifaceted approach that combines medical treatments, natural remedies, and lifestyle adjustments for holistic management. For atopic dermatitis, topical treatments are often the first line of defense. These may include corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and itching, as well as moisturizers to hydrate and repair the skin barrier. In more severe cases, systemic therapies such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologic medications may be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Seborrheic dermatitis scalp eczema can be managed with medicated shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or coal tar to reduce yeast overgrowth and inflammation. Topical corticosteroids or antifungal creams may also be recommended for more stubborn cases. Lifestyle adjustments, such as avoiding harsh hair products and minimizing stress, can also help manage flare-ups.
Contact dermatitis on the scalp often requires identifying and avoiding the triggering allergens or irritants. This may involve switching to fragrance-free, essential oil-free, and irritant-free hair care products, as well as avoiding certain metals or chemicals found in hair dyes or styling products. Essential oils should be used cautiously, if at all, as they can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Fragrance should also be avoided, as it is known to be a top allergen in cosmetics. Remember to patch-test any new products or ingredients to ensure they don't cause irritation or allergic reactions. You can learn more about common allergens in cosmetics in this study.
 Contact dermatitis. Image credits
Contact dermatitis. Image credits
Lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in holistic management of scalp eczema. This includes practicing good scalp hygiene, avoiding scratching or picking at the scalp, managing stress through relaxation techniques or therapy, and maintaining a healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
Overall, a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments, natural remedies, and lifestyle adjustments is key to effectively managing and reducing the symptoms of scalp eczema. Working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan and regularly monitoring progress is essential for long-term success.
Managing Eczema on Head under Hair: Daily Care and Prevention
Managing eczema in hair requires a daily care routine tailored to soothe and prevent flare-ups. Start by choosing gentle, hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and irritant-free hair care products that won't exacerbate eczema symptoms. A non-medicated, gentle shampoo like Just Shampoo by The Better Scalp Company is recommended due to its mild formulation suitable for sensitive scalps. When washing your hair, use lukewarm water and avoid scrubbing vigorously to prevent further irritation. Regardless of the type of eczema, it's crucial to avoid hot water when washing the hair, as it can strip the scalp of natural oils and exacerbate dryness. After washing, gently pat your hair dry with a soft towel, avoiding rubbing, which can aggravate eczema-prone areas.
For seborrheic dermatitis, use a medicated shampoo containing ingredients like ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or coal tar to target yeast overgrowth and reduce inflammation. Follow the instructions on the shampoo label for frequency of use and leave-on time before rinsing.
In addition to daily care, proactive measures can help manage eczema flare-ups. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can reduce stress-related triggers. Identifying and avoiding known triggers like harsh weather conditions, certain fabrics, or specific foods can also help prevent flare-ups.

By implementing a gentle hair care routine, using recommended products like Just Shampoo by The Better Scalp Company, and taking proactive measures to manage stress and avoid triggers, you can effectively manage and prevent eczema flare-ups in your hair. Consistency and patience are key, so stick to your tailored routine and consult with a dermatologist if you have persistent or severe symptoms.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help for scalp eczema is crucial in managing the condition effectively. If you notice persistent or worsening symptoms despite following a gentle hair care routine and using recommended products, it may be time to consult a dermatologist. Signs that your condition may require more advanced intervention include severe itching, inflammation, oozing or crusting of the scalp, and significant hair loss.
A dermatologist can assess your scalp eczema and recommend appropriate treatments, such as prescription-strength corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, or phototherapy (light therapy) to control inflammation and relieve symptoms. Some dermatologists can perform patch tests, which may be necessary especially if your scalp eczema is suspected to be triggered by allergens in your environment or hair care products. Patch testing can help pinpoint allergens and guide you in making informed choices about product selection and environmental modifications.
Beyond dermatologists, other healthcare professionals such as trichologists (hair and scalp specialists) or immunologists may be involved in the spectrum of care for severe or complex cases of eczema on scalp. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team can provide comprehensive and tailored management strategies to improve your scalp health and quality of life. If you're unsure about when to seek professional help, it's always best to err on the side of caution and schedule a consultation with a healthcare provider specializing in dermatology or skin allergies.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, managing scalp eczema requires a multifaceted approach in understanding symptoms, causes, and treatment options. It's vital to recognize the diverse triggers like genetic predisposition, allergens, irritants in hair care products, stress, and fungal or bacterial infections that can exacerbate eczema on the head. Education and community support play a crucial role in navigating this challenging condition. Additionally, adopting a gentle daily care routine, using hypoallergenic and fragrance-free hair care products like Just Shampoo by The Better Scalp Company, and practicing proactive measures such as stress management and avoiding known triggers are key steps in managing scalp eczema effectively. Ongoing education and seeking professional help when necessary are essential components that empower individuals to take control of their scalp health and improve their overall quality of life.
Scalp Eczema: Frequently Asked Questions
What is eczema on the scalp?
Eczema on the scalp refers to a group of inflammatory skin conditions affecting the scalp beneath the hair, including atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. These conditions are characterized by symptoms such as redness, itching, flaking, and sometimes oozing or crusting.
Can eczema occur in hair, and how does it look?
Yes, eczema can occur in the hair and scalp. It may appear as redness, flakiness, or scaling on the scalp, and in severe cases, it can lead to hair loss due to scratching and irritation.
What causes eczema on head under hair?
The causes of scalp eczema vary depending on the specific type. Atopic dermatitis is often linked to genetics, seborrheic dermatitis is associated with an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast and excessive oil production, and contact dermatitis arises from direct contact with irritants or allergens in hair care products or other substances.
How can I tell if I have eczema or dandruff in my hair?
Eczema and dandruff can have similar symptoms like flaking and itching, but they have distinct differences. Dandruff primarily involves flaking due to an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, while eczema can present with inflammation, redness, and sometimes oozing or crusting in addition to flaking.
How to treat eczema on scalp?
Treatment for eczema on the scalp involves a multifaceted approach, including topical treatments like corticosteroid creams or shampoos containing ingredients to target yeast overgrowth or inflammation. Lifestyle adjustments, such as managing stress and using gentle hair care products like Just Shampoo by The Better Scalp Company are also essential.
Are there any home remedies for managing scalp eczema?
Some home remedies may help manage scalp eczema, such as applying aloe vera gel, taking oatmeal baths, or using fragrance-free hypoallergenic products can soothe itching and inflammation. However, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Can changes in diet help with eczema?
While there's no specific diet to cure eczema, some people find that certain dietary changes, such as reducing dairy or gluten intake, can help manage symptoms. Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants may also benefit overall skin health.
Is it possible to prevent eczema flare-ups?
Preventing eczema flare-ups involves identifying and avoiding triggers like allergens, irritants, stress, and harsh hair care products. Maintaining good scalp hygiene, using hypoallergenic and fragrance-free hair care products like the ones from The Better Scalp Company, and managing stress can help minimize flare-ups.
When should I see a doctor for eczema on my scalp?
It's essential to see a doctor if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms of scalp eczema, such as severe itching, inflammation, oozing or crusting, or significant hair loss. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatments.
Can eczema on the scalp lead to hair loss?
Severe eczema on the scalp, characterized by intense scratching and irritation, can lead to temporary hair loss. However, with proper management and treatment, including addressing the underlying causes and avoiding triggers, hair loss can often be minimized or reversed.




